Supercritical Fluids
Introduction to Supercritical Fluids
Supercritical fluids represent a fascinating state of matter that defies traditional classifications. While we are familiar with solids, liquids, and gases in our daily lives, supercritical fluids occupy a unique position, displaying properties of both liquids and gases. In this article, we delve into the realm of supercritical fluids, exploring their characteristics, behaviors, and applications.
Understanding Phase Diagrams
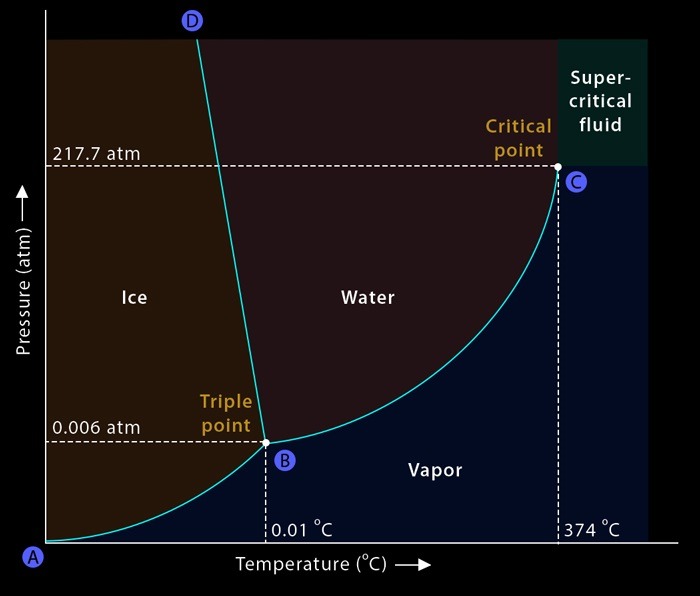
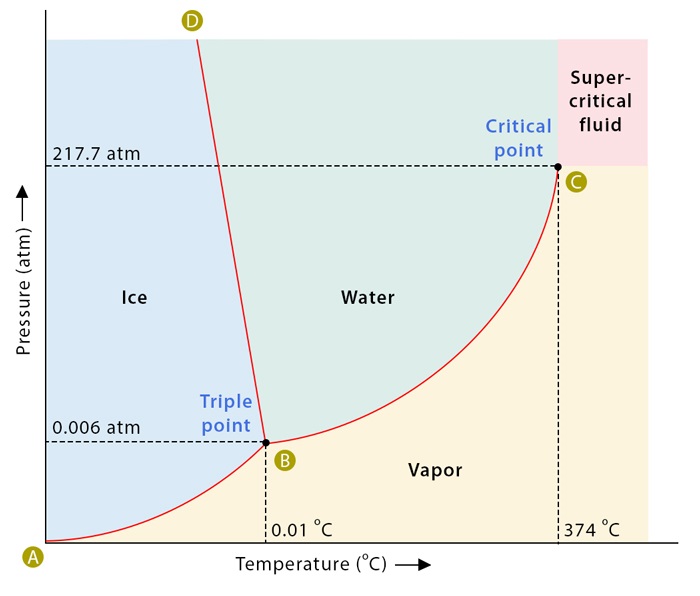
To comprehend supercritical fluids, we must first grasp the concept of phase diagrams. These diagrams illustrate the relationship between temperature, pressure, and the phase of a substance. Utilizing a tightly sealed container and adjusting temperature and pressure parameters, scientists can replicate various conditions to observe the behavior of substances like water. Through meticulous experimentation, phase diagrams reveal the boundaries and transitions between solid, liquid, and gas phases.
Reaching the Critical Point
At the heart of understanding supercritical fluids lies the critical point, where the distinction between liquid and gas blurs. By heating and compressing a substance like water within a controlled environment, researchers can approach this critical point. As temperature and pressure reach critical values, the substance undergoes a remarkable transformation, exhibiting properties of both liquids and gases simultaneously.
Properties and Applications
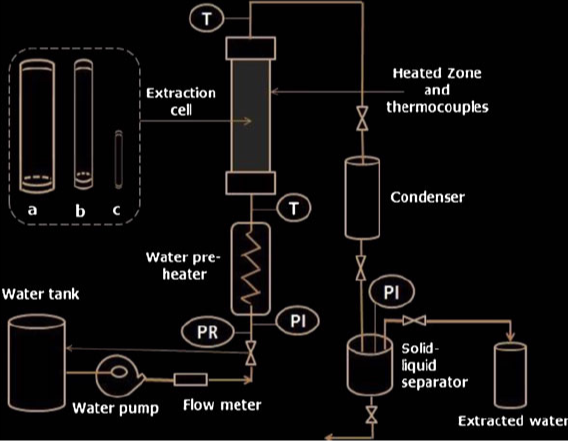
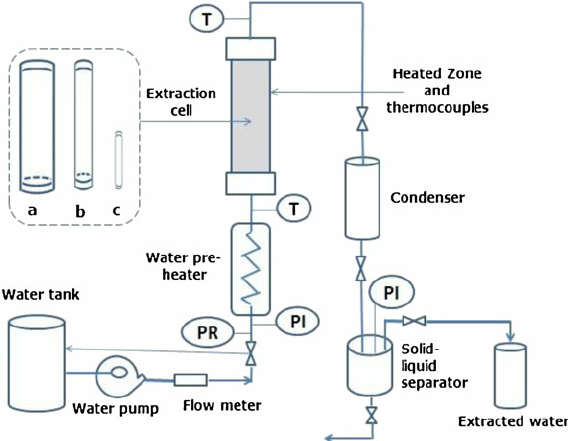
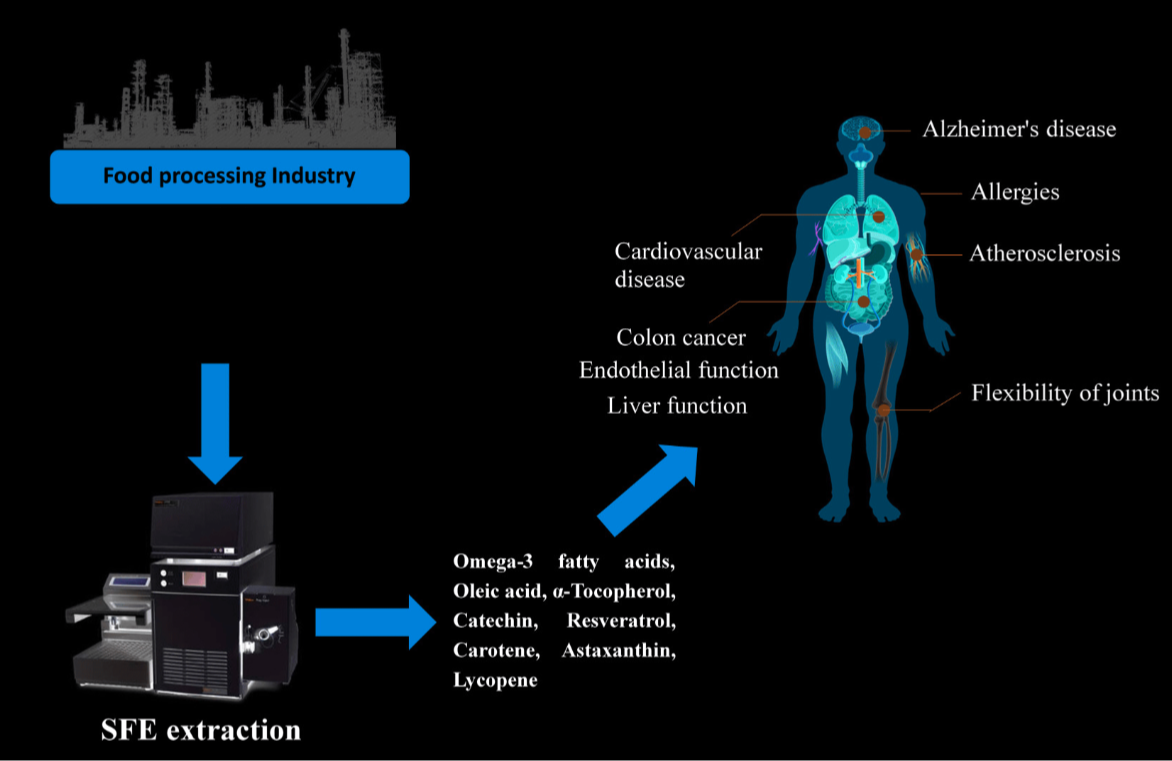
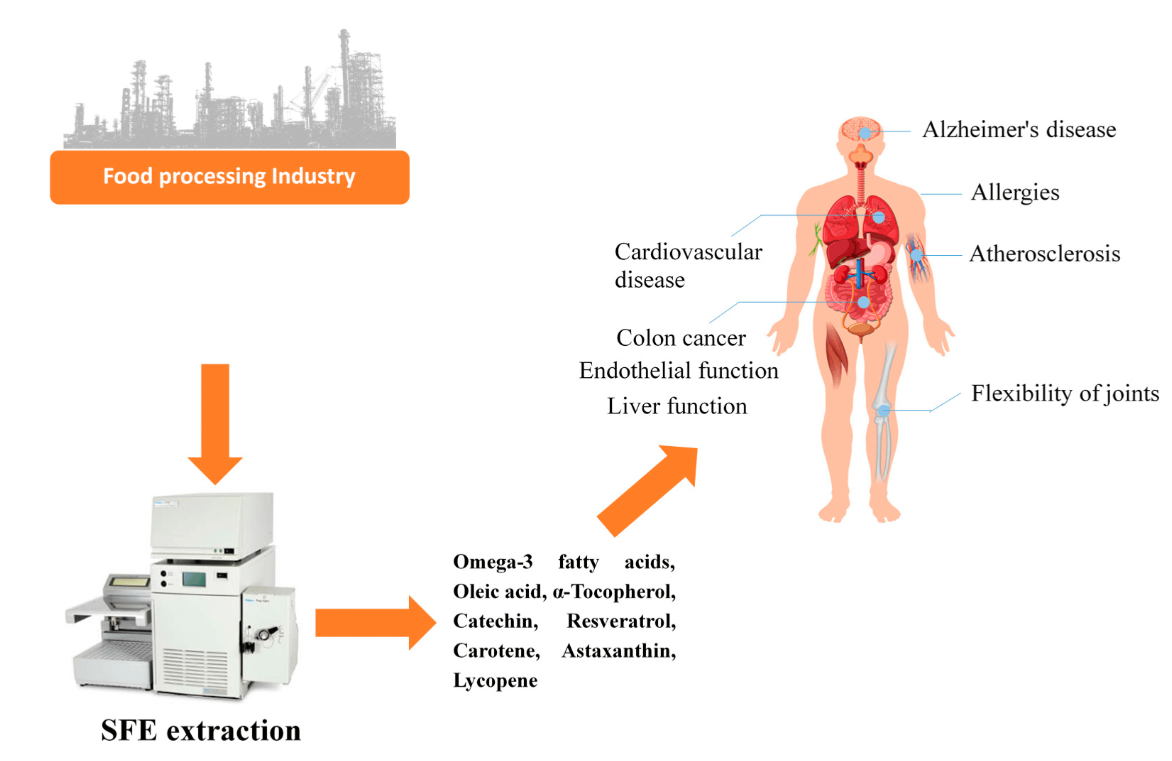
Supercritical fluids offer a diverse array of applications due to their unique properties. Despite behaving predominantly like gases, they can act as highly efficient solvents, facilitating the extraction of various substances from natural sources. Additionally, their non-toxic nature and high extraction power make them invaluable in industries such as food production, pharmaceuticals, and environmental remediation.
Conclusion and Implications
In conclusion, supercritical fluids represent a frontier in materials science with far-reaching implications. While rare on Earth’s surface, they are abundant in extreme environments such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents and the atmospheres of distant planets. By harnessing their unique properties, scientists and engineers continue to unlock new possibilities in fields ranging from manufacturing to environmental protection.
In essence, the study of supercritical fluids not only expands our understanding of matter but also offers innovative solutions to pressing challenges in science and industry.